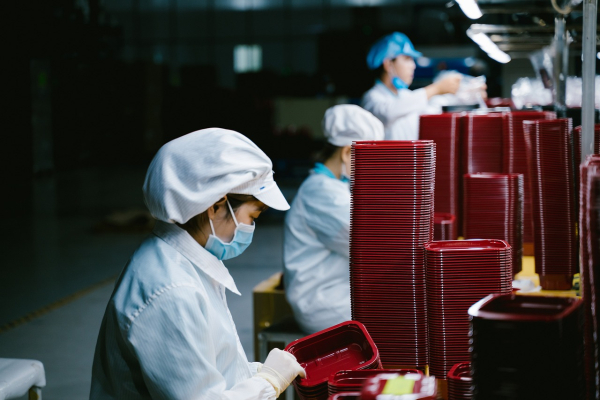
The evolving role of production workers
Traditionally, production workers were primarily involved in manual tasks, such as assembling products, operating machinery, and maintaining production lines. However, the modern production worker's role has expanded significantly. Today, they are expected to possess a blend of technical skills, problem-solving abilities, and adaptability to keep pace with technological advancements and shifting market demands. This evolution reflects the broader changes in the manufacturing sector, where automation and digitalization have transformed production processes.
Key responsibilities and tasks
Production worker are responsible for a wide array of tasks that ensure the seamless operation of manufacturing facilities. These responsibilities include:
- Operating machinery and equipment - Production workers must be proficient in handling various types of machinery, ensuring they are set up correctly and functioning optimally.
- Quality control - Monitoring products for defects and ensuring they meet established quality standards is a crucial aspect of their role.
- Maintenance and troubleshooting - Identifying and addressing mechanical issues promptly to minimize downtime and maintain production flow.
- Adhering to safety protocols - Following strict safety guidelines to prevent accidents and ensure a safe working environment for all employees.
- Collaborating with team members - Effective communication and teamwork are essential for coordinating tasks and achieving production goals.
Essential skills and qualifications
To excel in their roles, production workers must possess a combination of technical and soft skills. Key competencies include:
- Technical proficiency - Understanding the operation of machinery, tools, and production software is fundamental.
- Attention to detail - Precision is vital in tasks such as quality control and assembly to avoid errors that could compromise product integrity.
- Problem-solving abilities - The capacity to quickly identify issues and implement effective solutions is highly valued.
- Physical stamina - Many production roles require standing for extended periods, lifting heavy objects, and performing repetitive tasks.
- Adaptability - The ability to adjust to new technologies, processes, and production demands is increasingly important in a dynamic manufacturing environment.
Impact of technology on production workers
Advancements in technology have significantly influenced the role of production workers. Automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence have streamlined many manufacturing processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing the likelihood of human error. However, these technological shifts also present challenges and opportunities for production workers:
- Increased efficiency - Automated systems can perform repetitive tasks faster and with greater precision, allowing production workers to focus on more complex and value-added activities.
- Skill enhancement - The integration of advanced technologies necessitates ongoing training and skill development, enabling production workers to operate sophisticated machinery and utilize production software effectively.
- Job transformation - While automation may reduce the need for certain manual tasks, it also creates new roles that require technical expertise and problem-solving capabilities.
Safety and ergonomics in the workplace
Ensuring the safety and well-being of production workers is paramount in manufacturing settings. Employers must implement comprehensive safety protocols and invest in ergonomic solutions to minimize workplace hazards and prevent injuries. Key considerations include:
- Safety training-Regular training sessions on safety procedures, equipment handling, and emergency response can significantly reduce the risk of accidents.
- Ergonomic equipment - Providing adjustable workstations, ergonomic tools, and supportive footwear can alleviate physical strain and prevent musculoskeletal disorders.
- Preventive maintenance - Regular inspections and maintenance of machinery help identify potential issues before they escalate into safety hazards.
- Health and wellness programs - Initiatives that promote physical and mental well-being can enhance overall job satisfaction and productivity among production workers.
Training and professional development
Continuous training and professional development are essential for maintaining a skilled and adaptable workforce. Investing in the education and growth of production workers offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced productivity - Well-trained workers are more efficient and capable of producing higher-quality products.
- Employee retention - Opportunities for advancement and skill development can increase job satisfaction and reduce turnover rates.
- Innovation and improvement -Encouraging a culture of learning fosters innovation, as workers are more likely to contribute ideas for process enhancements and problem-solving.
Challenges faced by production workers
Despite the advancements in manufacturing, production workers encounter various challenges that can impact their performance and job satisfaction:
- Workplace stress - High production targets, tight deadlines, and the pressure to maintain quality can lead to stress and burnout.
- Job insecurity - The rise of automation and changing industry demands can create uncertainty regarding job stability and future opportunities.
- Physical demands - The physically demanding nature of many production roles can result in fatigue and long-term health issues.
- Adaptation to change - Keeping up with technological advancements and evolving production methods requires continuous learning and flexibility.
Strategies for supporting production workers
Employers can implement several strategies to support production workers and mitigate the challenges they face:
- Comprehensive training programs - Providing ongoing education and skills development ensures that workers remain proficient in their roles and can adapt to new technologies.
- Employee recognition - Acknowledging and rewarding the hard work and achievements of production workers can boost morale and motivation.
- Health and safety initiatives - Prioritizing workplace safety and offering health benefits contribute to the overall well-being of employees.
- Open communication channels - Encouraging transparent and open communication allows workers to voice concerns, share feedback, and collaborate effectively.
- Career advancement opportunities - Offering clear pathways for career progression can enhance job satisfaction and encourage long-term commitment to the organization.
Future trends and the role of production workers
The future of manufacturing is likely to be shaped by continued technological advancements, sustainability initiatives, and evolving market demands. Production workers will play a crucial role in navigating these trends:
- Sustainable manufacturing - Emphasizing eco-friendly practices and reducing waste will require production workers to adopt new methods and technologies that support sustainability goals.
- Smart manufacturing - The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and data analytics will enable more efficient and responsive production processes, with production workers leveraging real-time data to optimize operations.
- Customization and flexibility - As consumer preferences shift towards personalized products, production workers will need to adapt to more flexible and versatile manufacturing systems that can accommodate customization without sacrificing efficiency.
Production workers are the backbone of the manufacturing industry, contributing to the efficiency, quality, and safety of production processes. As the sector continues to evolve, the role of the production worker will expand to encompass a broader range of skills and responsibilities. By investing in training, fostering a supportive work environment, and embracing technological advancements, manufacturers can empower production workers to thrive in a dynamic and competitive landscape. Recognizing the invaluable contributions of production workers and addressing their challenges is essential for sustaining growth and achieving long-term success in the manufacturing industry.